Inside the Deep Web: How Hidden Content Powers the Modern Internet
When people talk about the internet, they usually imagine search engines, social media platforms, and public websites that appear instantly in search results. In reality, this visible layer represents only a small fraction of what exists online. Beneath it lies the deep web, a vast network of hidden content that supports daily digital life. One of the most commonly mentioned directories within discussions about hidden resources is the hidden wiki, often referenced when explaining how users navigate non-indexed areas of the web. Understanding this hidden layer is essential to understanding how the modern internet actually functions.
What the Deep Web Really Is
The deep web refers to any online content that is not indexed by standard search engines like Google or Bing. This does not mean it is secret, illegal, or dangerous. In fact, most people use the deep web every single day without realizing it.
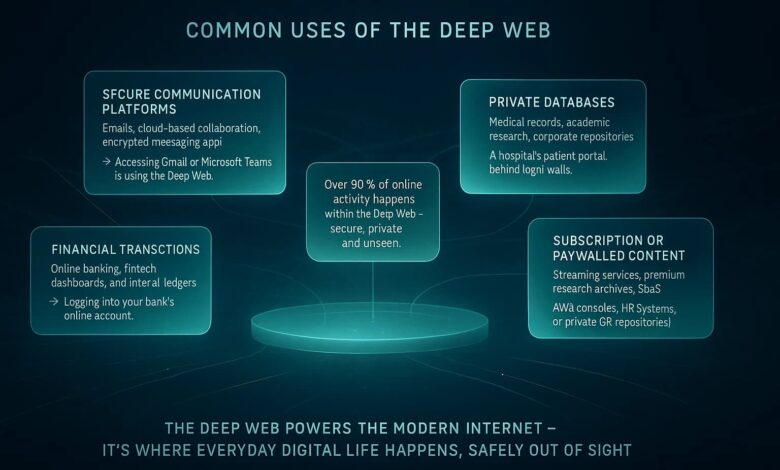
Email inboxes, online banking portals, cloud storage accounts, academic databases, private company dashboards, and subscription-based platforms are all part of the deep web. These areas are protected by logins or permissions, which prevent search engines from crawling and displaying their content publicly.
Without the deep web, basic digital services would not function securely. Privacy, authentication, and data protection all depend on keeping certain information out of public search results.
The Difference Between the Deep Web and the Dark Web
The terms deep web and dark web are often confused, but they are not the same. The deep web includes all private or restricted-access content. The dark web is a small subsection of the deep web that requires special software, such as Tor, to access.
While the dark web receives media attention for illicit activity, it also hosts legitimate uses such as anonymous journalism, whistleblowing platforms, and privacy-focused communication. However, the majority of the deep web has nothing to do with anonymity tools or hidden networks. It exists simply to protect user data and system integrity.
Understanding this distinction is important. Equating the deep web with criminal activity is inaccurate and misleading.
Why So Much of the Internet Is Hidden
Search engines are designed to index public pages that can be freely accessed. Any page that requires a login, form submission, or specific permission is excluded by design. This ensures that sensitive data is not accidentally exposed.
Businesses rely on the deep web to manage internal operations. Hospitals store patient records in secure databases. Universities host research papers behind paywalls. Governments protect citizen data within restricted systems.
These hidden layers allow organizations to operate efficiently while complying with privacy laws and ethical standards. Without them, the internet would be chaotic and unsafe.
The Role of Directories in Hidden Content Navigation
Because deep web content is not searchable in traditional ways, users rely on direct links, portals, and directories to access it. Historically, directories have helped users understand where certain types of information are located.
In discussions about non-indexed content and onion-based networks, the hidden wiki is often mentioned as an example of how directories organize links for users exploring less visible parts of the internet. Such directories act as maps rather than search engines, offering structured access instead of indexed results.
It is important to approach any directory with caution and critical thinking, as content quality and safety vary widely.
How Hidden Content Supports Everyday Digital Life
The modern internet would collapse without hidden systems working behind the scenes. When you log into your bank account, stream content on a paid platform, or access work files remotely, you are using the deep web.
E-commerce platforms depend on hidden databases to manage orders and payments. Messaging apps store conversations in private servers. Medical systems rely on restricted access to protect patient confidentiality.
These systems are not hidden to be mysterious. They are hidden to be secure, reliable, and compliant with regulations.
Privacy and Security in the Deep Web
One of the biggest advantages of the deep web is privacy. By keeping personal data behind authentication barriers, users gain control over who can see their information.
Security protocols such as encryption, session management, and access control are fundamental to deep web infrastructure. These technologies prevent unauthorized access and data leaks.
As privacy concerns grow worldwide, the deep web becomes even more important. It enables safe communication, protects financial systems, and ensures that sensitive information remains confidential.
Common Myths About Hidden Internet Content
Many myths surround hidden content online. One common belief is that anything hidden from search engines is suspicious. In reality, hiding content is a standard security practice.
Another misconception is that accessing hidden resources is illegal. Accessing private content without permission is illegal, but using secure platforms or reading restricted academic material with proper credentials is completely lawful.
Education plays a key role in separating fact from fiction. When people understand how the internet is structured, fear-based narratives lose their power.
Why Understanding the Deep Web Matters
Digital literacy is no longer optional. Understanding how hidden systems operate helps users make informed decisions about privacy, security, and online behavior.
Knowing what the deep web is can reduce unnecessary fear and encourage responsible internet use. It also highlights the importance of protecting personal data and respecting access boundaries.
As technology evolves, hidden content will continue to expand. Cloud services, remote work platforms, and digital identity systems all depend on deep web architecture.
Final Thoughts: The Internet You Don’t See Still Runs Everything
The internet is far more than what appears on search engine result pages. Behind every public website is a hidden framework that manages data, privacy, and access. From personal emails to global financial systems, the deep web powers the digital world quietly and efficiently.
Resources like the hidden wiki are often referenced when discussing how hidden content is organized and accessed, but the true value lies in understanding the concept rather than exploring blindly. When viewed correctly, the deep web is not a shadowy place but the backbone of modern online life.
By learning how hidden content works, users gain a clearer, safer, and more realistic view of the internet they rely on every day.
